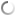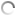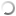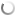|
| Super pit gold mine is the largest open pit mine |
Kalgoorlie mine In Australia or better known as the Super Pit is located off the Goldfields Highway on the south-east edge of Kalgoorlie, Western Australia. Super pit gold mine is the largest open pit mine which has a hole a length of about 3.5 kilometers, 1.5 kilometres wide and 570 metres deep that make up the rectangle.
The Super Pit gold mine is owned by Kalgoorlie Consolidated Gold Mines Pty Ltd, a company owned two joint venture between Barrick Gold Corporation and Newmont Mining Corporation with respective shares of 50%
Kalgoorlie Consolidated Gold Mines Pty Ltd (KCGM) was formed to manage the assets and operations of joint venture partners, Normandy Australia and Homestake Gold of Australia Limited.
MINERAL DEPOSIT IN SUPER PIT GOLD MINE
 |
| Mineral deposit in super pit gold mine |
The main host rock for mineralisation the Kalgoorlie district in Super Pit gold mine is the Golden Mile Dolerite, the largest of the dolerites in the area. There are two main styles of mineralisation. The Fimiston Style consists of classic Golden Mile lodes with abundant sulphides and tellurides. The Charlotte Style describes younger white quartz veins which are typically mined at Mt Charlotte, but have been found in other smaller deposits in the Kalgoorlie District.
The Golden Mile lodes have several characteristic orientations, each with slight variations in the style of the mineralisation. More than 1,000 individual ore lodes occur within the Golden Mile, some extending up to 1,800 metres long, 1,200 metres deep and 10 metres wide. They are all within an area over five kilometres long, two kilometres wide and more than one kilometre deep. The highest gold grades are typically associated with gold tellurides and alteration minerals with high vanadium contents.
PROCESS OF MINING IN SUPER PIT GOLD MINE AUSTRALIA
The early stages of the mining process is the process of drilling to insert explosives. Blasting in Super Pit gold mine is usually conducted three or four times a week between 7am and 6pm.
Blasting mining process is a process of destruction and decomposition of rocks in the soil to rock minerals can be easily taken up and transported
To prepare a blast pattern, detonators and primers are lowered into the 11.5 metre drill holes and liquid explosive, a mixture of ammonium nitrate and diesel called “bomb”, is pumped in inserted into the hole as deep as 4 meters. The hole is then filled with stemming – screened gravel – to act as a plug and force the explosive energy down and into the surrounding rock.
Before the ore can be dug in the blasting area, geologists mark blast site, pegging and flagging the blocks of ore and waste rock. From this they produce a “dig plan” which is sent electronically to the onboard navigation systems of the shovels which will load the ore and waste rock into haul trucks.
The shovels and trucks PC8000 hydraulic face shovel and 750-tonne Komatsu moves in Pit floor. The shovel operator notifies the dispatch operator in the WENCO hut, Navigation programme shows the operator, what type of material and the shovel in mining. This may be ore, marginal subgrade material or waste, who then updates the computer with the material type and its eventual destination.
The dispatch system then uploads information on the type of load the shovel is digging and where the truck driver is to take its load. This information is displayed on a screen on the cab’s dashboard for the driver.
Once the 240-tonne capacity truck is full, the dispatch system directs the driver to its destination. If the load is clean high grade ore, it will either be directly taken to the ROM (run of mine) pad at the Primary Crusher, or unloaded to a stockpile on Pad 12 for feed into the CSI Crusher. Then crusher reduces it to mineral rock chunks about the size of a fist.
Mineral ore is then inserted into SAG (Semi Autogenous Grinding) to make smaller. mineral rocks . To make very fine particles less than one-fifth of the diameter of one millimeter, the ore is put into the Ball Mills which look like huge steel drums rotating, adding water to do to make the mineral ore become a pulp.
 |
| Blasting mining process in Super Pit mine Australia |
 |
| Drilling to insert explosives in Super Pit Mine Australia |
The early stages of the mining process is the process of drilling to insert explosives. Blasting in Super Pit gold mine is usually conducted three or four times a week between 7am and 6pm.
Blasting mining process is a process of destruction and decomposition of rocks in the soil to rock minerals can be easily taken up and transported
To prepare a blast pattern, detonators and primers are lowered into the 11.5 metre drill holes and liquid explosive, a mixture of ammonium nitrate and diesel called “bomb”, is pumped in inserted into the hole as deep as 4 meters. The hole is then filled with stemming – screened gravel – to act as a plug and force the explosive energy down and into the surrounding rock.
 |
| PC8000 shovel scraper rock minerals to be loaded into the Haul truck |
The shovels and trucks PC8000 hydraulic face shovel and 750-tonne Komatsu moves in Pit floor. The shovel operator notifies the dispatch operator in the WENCO hut, Navigation programme shows the operator, what type of material and the shovel in mining. This may be ore, marginal subgrade material or waste, who then updates the computer with the material type and its eventual destination.
 |
| Haul truck load of rock minerals that will be sent to a processing |
Once the 240-tonne capacity truck is full, the dispatch system directs the driver to its destination. If the load is clean high grade ore, it will either be directly taken to the ROM (run of mine) pad at the Primary Crusher, or unloaded to a stockpile on Pad 12 for feed into the CSI Crusher. Then crusher reduces it to mineral rock chunks about the size of a fist.
 |
| Ball mill processing mineral ore |
GOLD ORE PROCESS IN SUPER PIT GOLD MINE AUSTRALIA
Flotation Processing In Super Pit mine Australia
 |
| Mineral ore processing into the flotation process |
Of a ball mill processing mineral ore is then transferred into a flotation cells , Slurry is then pumped into large tanks called flotation cells.
Air is added to the bottom of the agitating flotation cells and the resulting froth which gathers at the top contains nearly all the gold. This combination of free gold, gold-bearing pyrite and telluride particles is known as sulphide concentrate.
 |
| The dried concentrate |
The concentrate was also treated in one of two circulating fluid bed roasters at 650°C. Commissioning of the 30tph UFG Mill completely replaced roasting, eliminating atmospheric emissions from the Gidji Processing Plant.
Carbon In Pulp Process For Gold Recovery
 |
| The Carbon In Pulp (CIP) process |
The resultant concentrated or “pregnant” solution is subjected to electrolysis to remove the gold. Two electrowinning circuits are used at the Fimiston Plant for the recovery of gold from the high-grade solutions produced by the elution circuits. One circuit is dedicated to electrowinning the gold from the concentrate leach circuits, and the other electrowins the gold from the flotation tails leach circuit.
When all the gold has been recovered from the solution, the “barren” solution is pumped back into the leach circuit. The gold sludge is removed periodically from the cathodes by high pressure water spraying. The collected sludge is filtered and dried.
 |
| Recovery of gold from the high-grade solutions on electrowinning |
Electrowinning is the recovery of metals, such as gold and silver, from solution by passing a current through the solution. Electrons from the current chemically reduce the gold and/or silver ions, to form a solid metal compound on the cathode.
Stainless steel wool is used as one electrode and stainless steel plates as the other. An electric current is passed through the solution and the gold is electrochemically plated onto the stainless steel wool. When all the gold has been recovered from the solution, then solution is pumped back into the leach circuit.
 |
| Smelting process using furnace for made gold bar |
Gold is purified by means of a smelting process, which utilizes pressure, high heat and chemicals. for smelting process using furnace.
When the molten mixture has reached more than 1,000°C the metal and slag are tipped into an ingot mould. The slag hardens into glass, leaving the gold ingot of 300 to 500 ounces in the bottom of the mould.
These gold bars, known as doré, are about 60% to 80% pure gold, with the rest consisting mainly of silver. Each bar is stamped with its own unique number, then the bars are transported to the Australian Gold Refinery at the Perth Mint where they are further refined to 99.9% pure gold